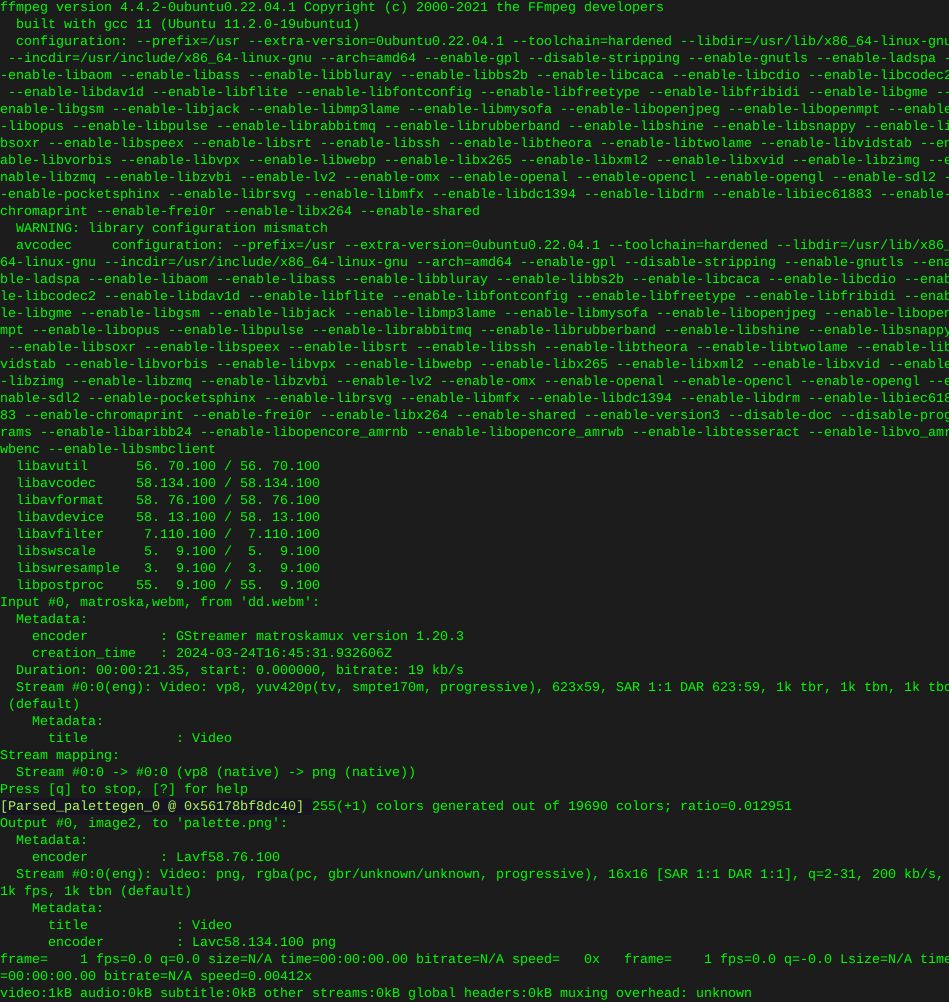
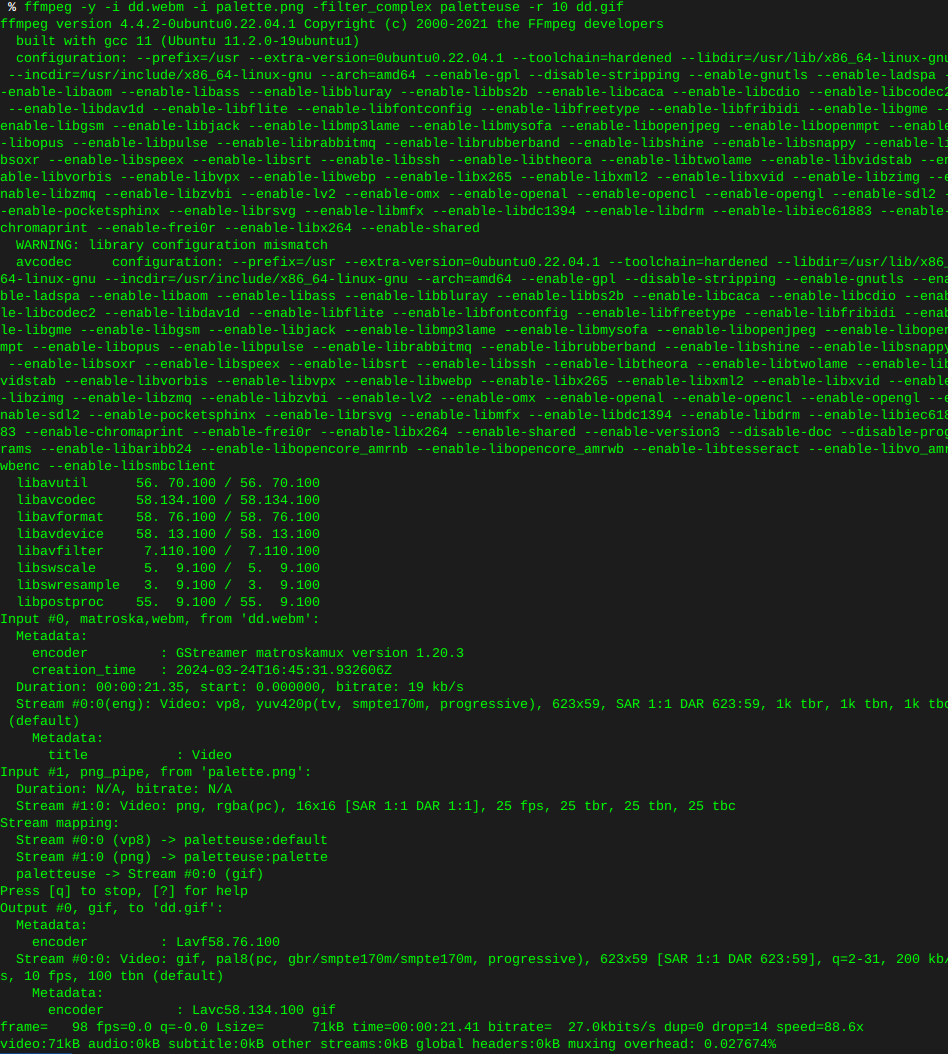
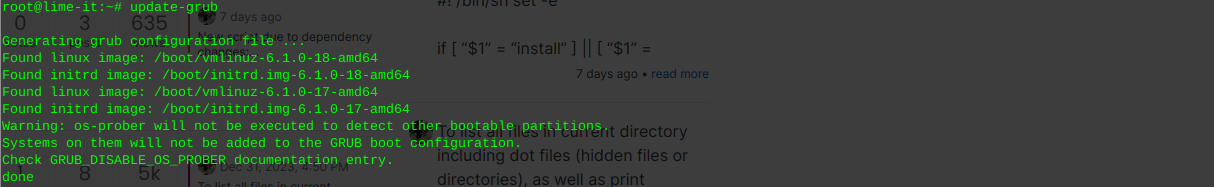
Locate hard drive and get information
ls -l /sys/block | grep sd.Output:
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jun 22 06:28 sda -> ../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1f.2/ata1/host0/target0:0:0/0:0:0:0/block/sda lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jun 22 06:28 sdb -> ../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1f.2/ata2/host1/target1:0:0/1:0:0:0/block/sdb lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jun 22 06:28 sdc -> ../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1f.2/ata3/host2/target2:0:0/2:0:0:0/block/sdc lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jun 22 06:28 sdd -> ../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1f.2/ata4/host3/target3:0:0/3:0:0:0/block/sddOr for a more detailed view
strace -e trace=open lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 3.6T 0 disk ├─data--2-data--2_tmeta 252:3 0 15.9G 0 lvm │ └─data--2-data--2-tpool 252:9 0 3.6T 0 lvm │ ├─data--2-data--2 252:10 0 3.6T 1 lvm │ ├─data--2-vm--101--disk--0 252:11 0 8G 0 lvm │ ├─data--2-vm--103--disk--0 252:12 0 32G 0 lvm │ ├─data--2-vm--107--disk--0 252:13 0 500G 0 lvm │ └─data--2-vm--108--disk--0 252:20 0 100G 0 lvm └─data--2-data--2_tdata 252:6 0 3.6T 0 lvm └─data--2-data--2-tpool 252:9 0 3.6T 0 lvm ├─data--2-data--2 252:10 0 3.6T 1 lvm ├─data--2-vm--101--disk--0 252:11 0 8G 0 lvm ├─data--2-vm--103--disk--0 252:12 0 32G 0 lvm ├─data--2-vm--107--disk--0 252:13 0 500G 0 lvm └─data--2-vm--108--disk--0 252:20 0 100G 0 lvm sdb 8:16 0 698.6G 0 disk └─sdb1 8:17 0 698.6G 0 part /mnt/pve/backups sdc 8:32 0 3.6T 0 disk ├─vm--data-vm--data_tmeta 252:4 0 15.9G 0 lvm │ └─vm--data-vm--data-tpool 252:14 0 3.6T 0 lvm │ ├─vm--data-vm--data 252:15 0 3.6T 1 lvm │ ├─vm--data-vm--100--disk--0 252:16 0 270G 0 lvm │ ├─vm--data-vm--102--disk--0 252:17 0 100G 0 lvm │ ├─vm--data-vm--104--disk--0 252:18 0 25G 0 lvm │ └─vm--data-vm--106--disk--0 252:19 0 32G 0 lvm └─vm--data-vm--data_tdata 252:7 0 3.6T 0 lvm └─vm--data-vm--data-tpool 252:14 0 3.6T 0 lvm ├─vm--data-vm--data 252:15 0 3.6T 1 lvm ├─vm--data-vm--100--disk--0 252:16 0 270G 0 lvm ├─vm--data-vm--102--disk--0 252:17 0 100G 0 lvm ├─vm--data-vm--104--disk--0 252:18 0 25G 0 lvm └─vm--data-vm--106--disk--0 252:19 0 32G 0 lvm sdd 8:48 0 931.5G 0 disk ├─sdd1 8:49 0 1007K 0 part ├─sdd2 8:50 0 1G 0 part └─sdd3 8:51 0 930.5G 0 part ├─pve-swap 252:0 0 8G 0 lvm [SWAP] ├─pve-root 252:1 0 96G 0 lvm / ├─pve-data_tmeta 252:2 0 8.1G 0 lvm │ └─pve-data 252:8 0 794.3G 0 lvm └─pve-data_tdata 252:5 0 794.3G 0 lvm └─pve-data 252:8 0 794.3G 0 lvm +++ exited with 0 +++ cat /proc/partitions major minor #blocks name 8 0 3907018584 sda 8 16 732574584 sdb 8 17 732572672 sdb1 8 32 3907018584 sdc 8 48 976762584 sdd 8 49 1007 sdd1 8 50 1048576 sdd2 8 51 975712967 sdd3 252 0 8388608 dm-0 252 1 100663296 dm-1 252 2 8495104 dm-2 252 3 16650240 dm-3 252 4 16650240 dm-4 252 6 3873329152 dm-6 252 5 832888832 dm-5 252 7 3873329152 dm-7 252 8 832888832 dm-8 252 9 3873329152 dm-9 252 10 3873329152 dm-10 252 11 8388608 dm-11 252 12 33554432 dm-12 252 13 524288000 dm-13 252 14 3873329152 dm-14 252 15 3873329152 dm-15 252 16 283115520 dm-16 252 17 104857600 dm-17 252 18 26214400 dm-18 252 19 33554432 dm-19 252 20 104857600 dm-20Locate drive by serial and model information
hdparm -i /dev/sda /dev/sda: Model=WDC WD4000FYYZ-05UL1B0, FwRev=00.0NS05, SerialNo=WD-WCC132262513 Config={ HardSect NotMFM HdSw>15uSec SpinMotCtl Fixed DTR>5Mbs FmtGapReq } RawCHS=16383/16/63, TrkSize=0, SectSize=0, ECCbytes=0 BuffType=unknown, BuffSize=unknown, MaxMultSect=16, MultSect=off CurCHS=16383/16/63, CurSects=16514064, LBA=yes, LBAsects=7814037168 IORDY=on/off, tPIO={min:120,w/IORDY:120}, tDMA={min:120,rec:120} PIO modes: pio0 pio3 pio4 DMA modes: mdma0 mdma1 mdma2 UDMA modes: udma0 udma1 udma2 udma3 udma4 udma5 *udma6 AdvancedPM=yes: unknown setting WriteCache=disabled Drive conforms to: Unspecified: ATA/ATAPI-1,2,3,4,5,6,7 * signifies the current active mode