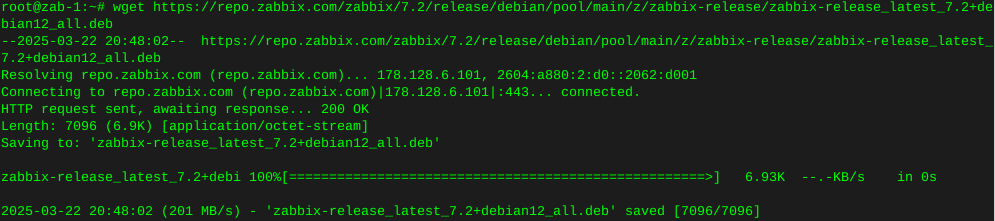
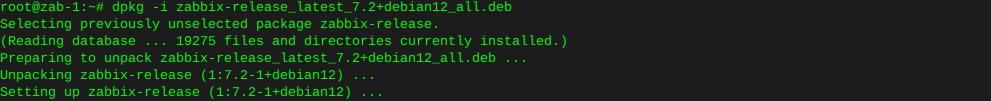
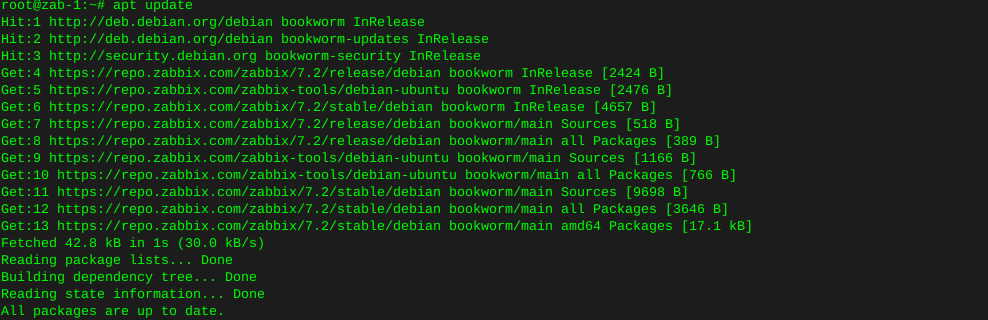
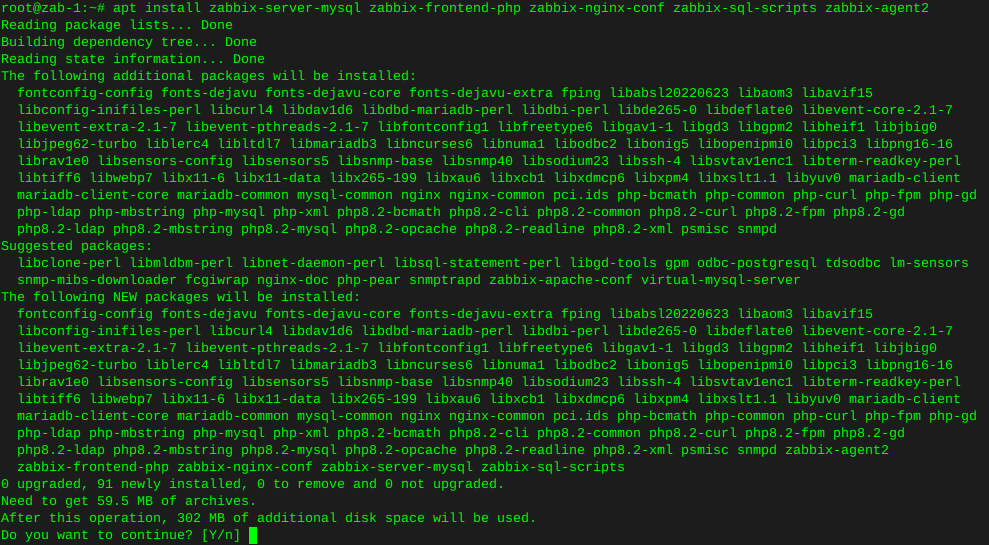
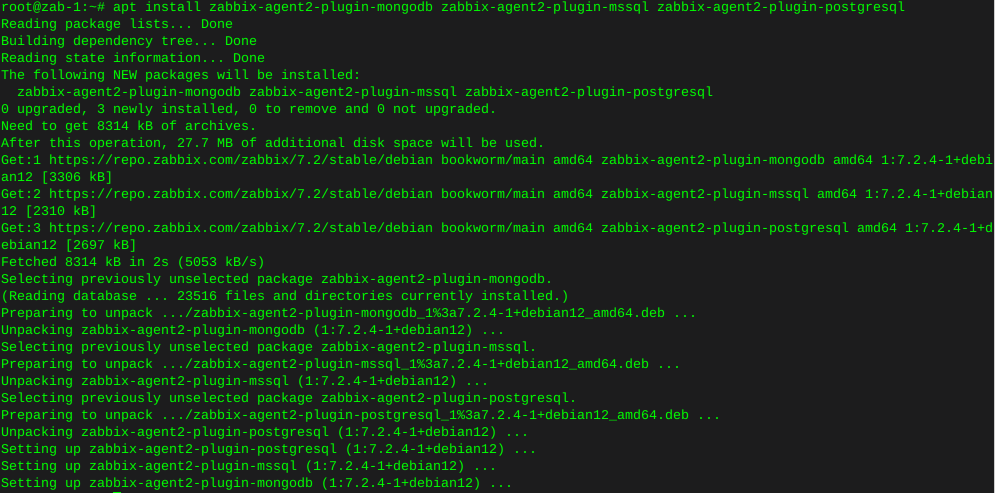
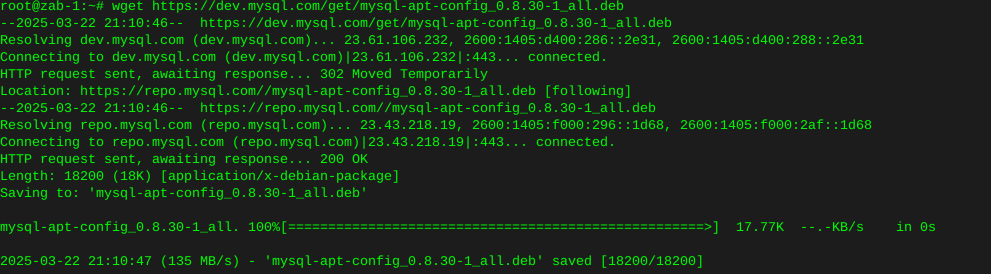
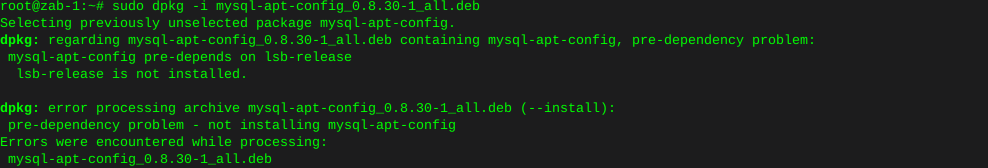
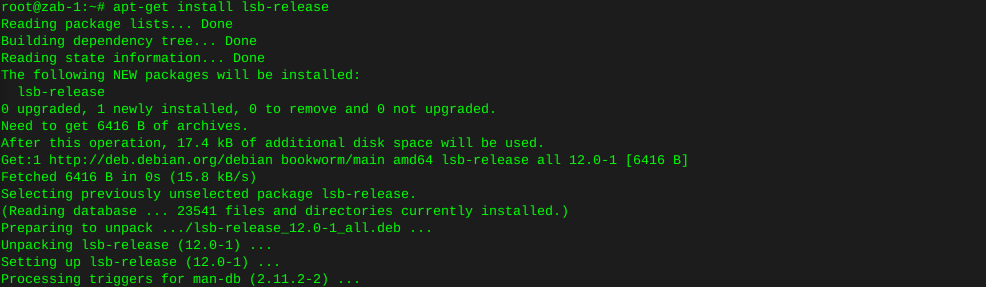
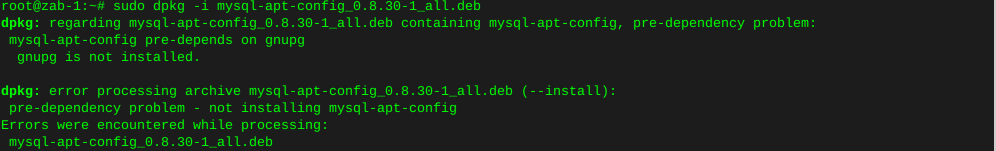
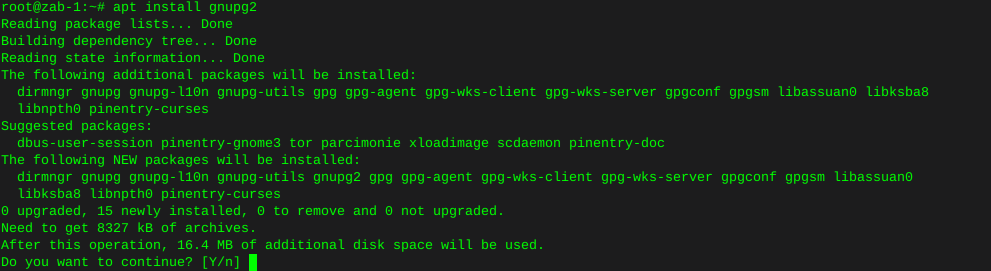
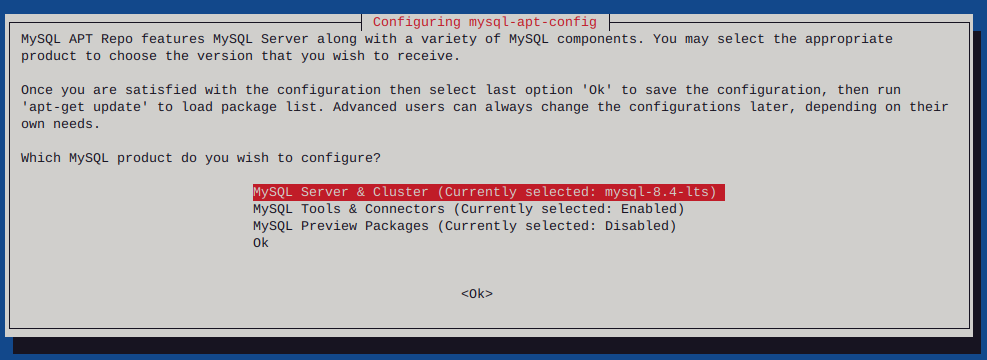
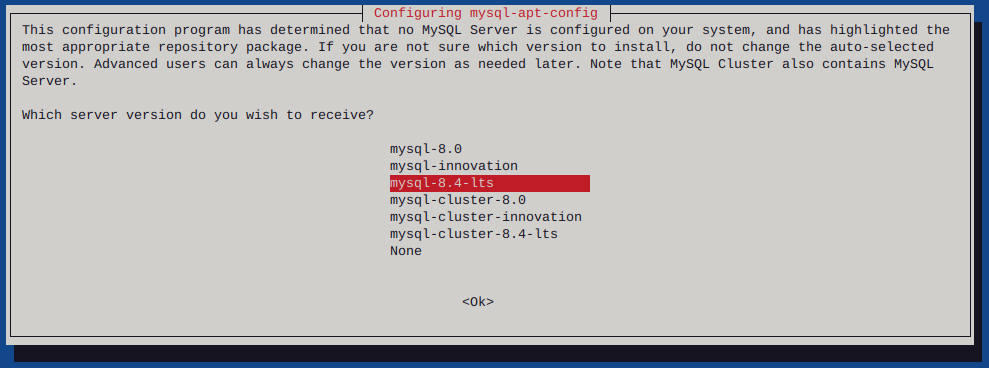
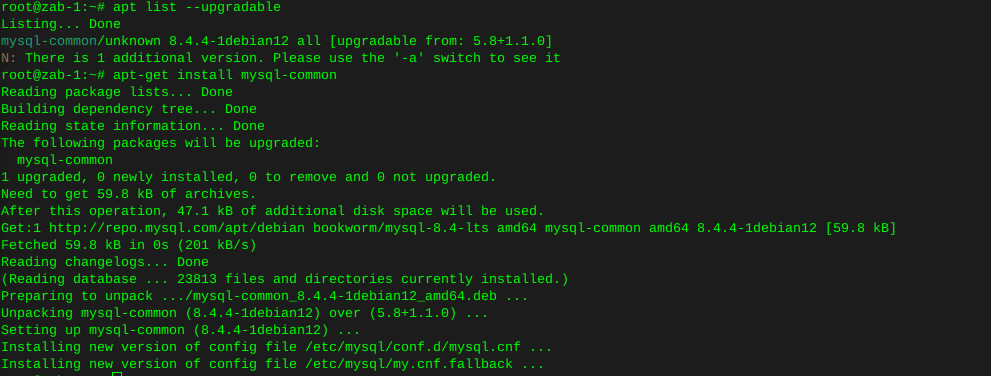
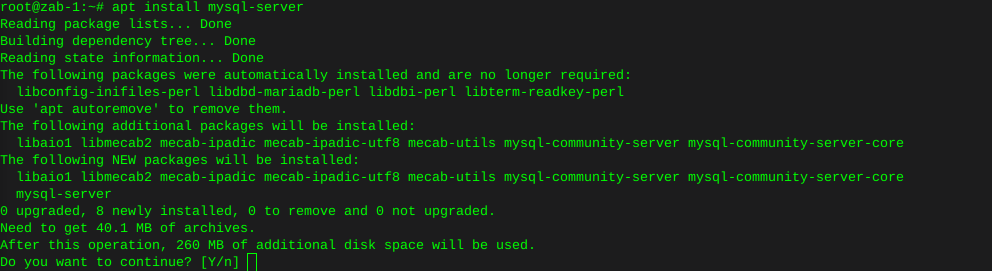
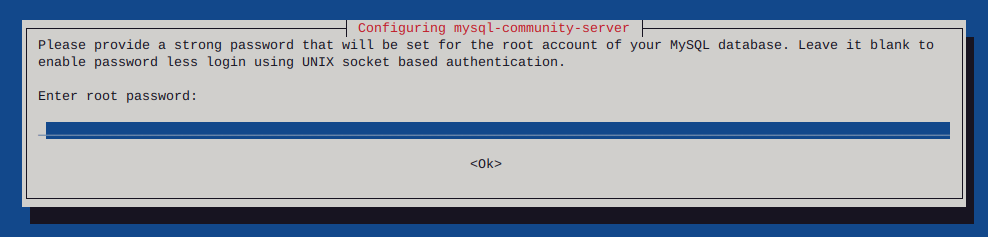
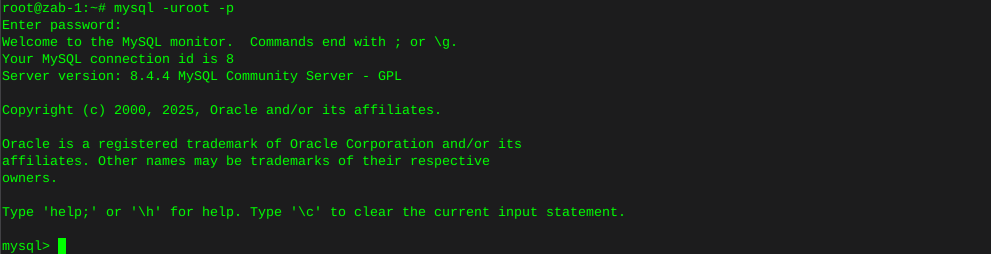
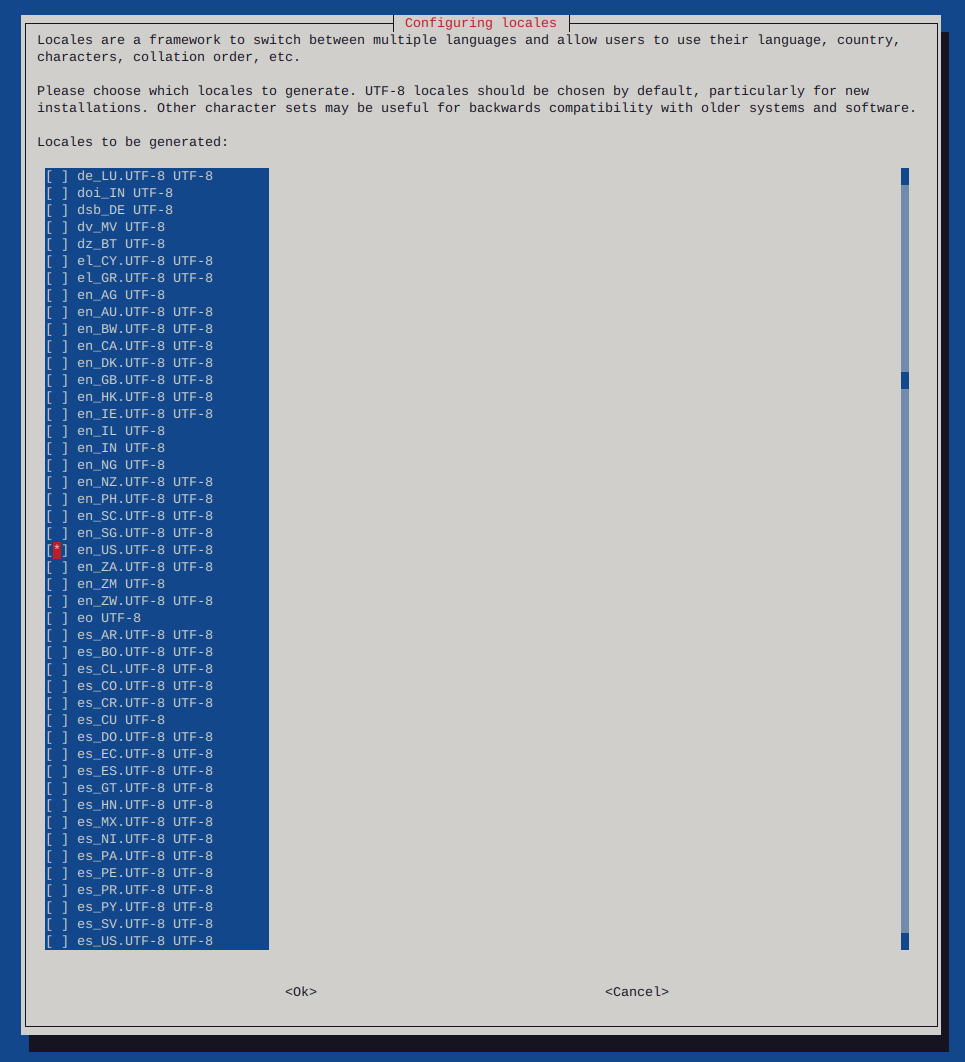
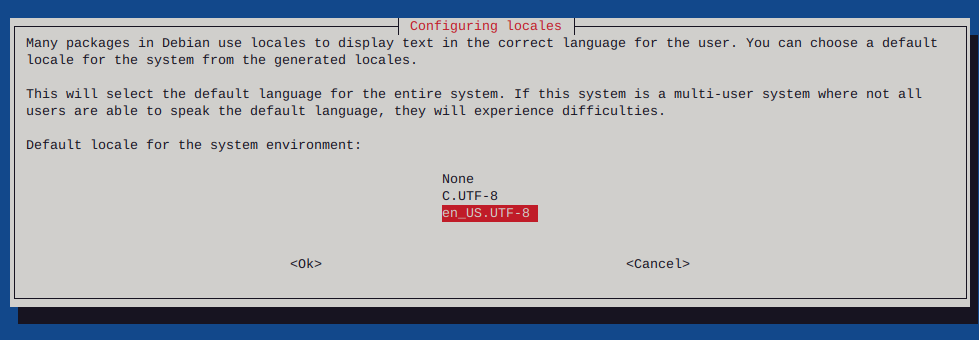
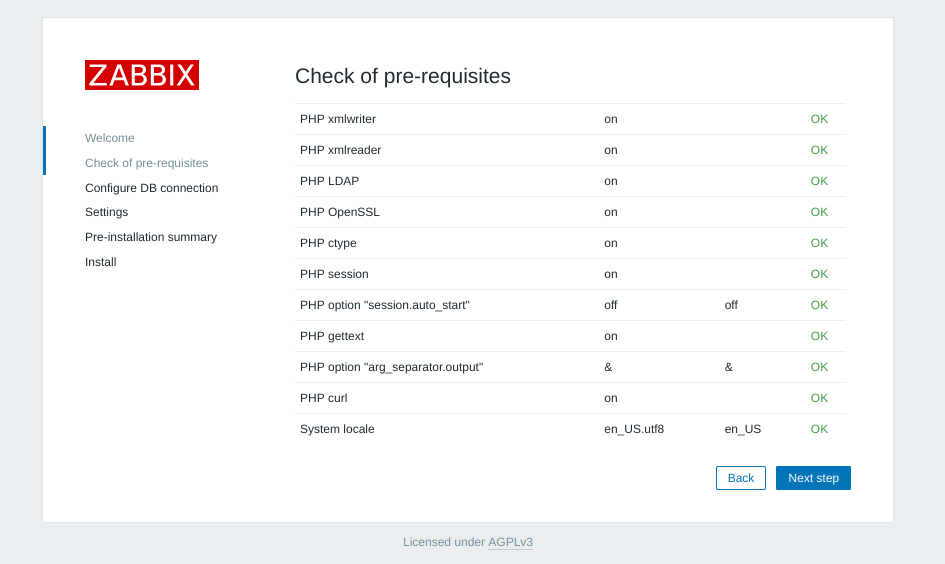
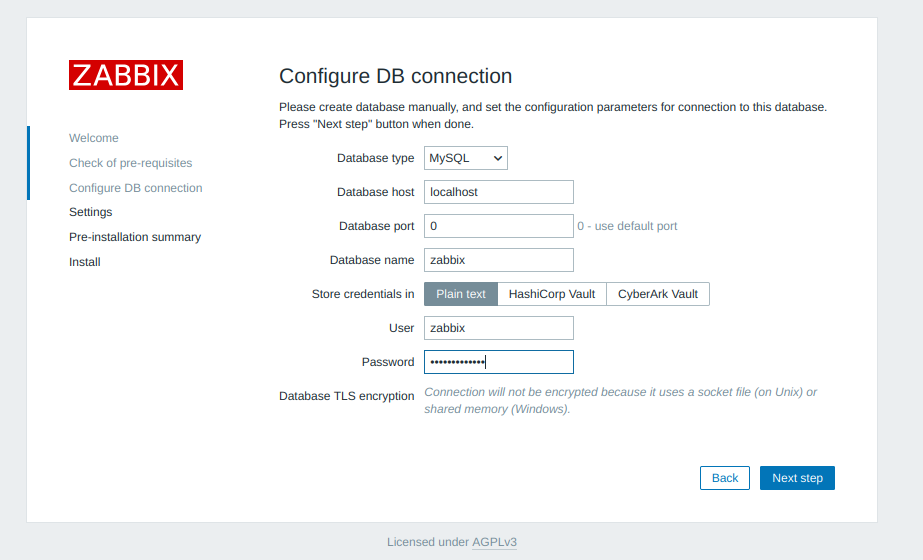
Http error codes
-
Error or Status Code Description
100 Series
Informational - These status codes indicate a provisional response. The client should be prepared to receive one or more 1xx responses before receiving a regular response.
100
Continue.
101
Switching protocols.
200 Series
Success - This class of status codes indicates that the server successfully accepted the client request.
200
The client request has succeeded. This status code indicates that the Web server has successfully processed the request.
201
Created.
202
Accepted.
203
Non-authoritative information.
204
No content.
205
Reset content.
206
Partial content.
300 Series
Redirection - The client browser must take more action to fulfill the request. For example, the browser may have to request a different page on the server or repeat the request by using a proxy server.
302
Object moved.
304
Not modified. The client requests a document that is already in its cache and the document has not been modified since it was cached. The client uses the cached copy of the document, instead of downloading it from the server
307
Temporary redirect.
400 Series
Client Error - An error occurs, and the client appears to be at fault. For example, the client may request a page that does not exist, or the client may not provide valid authentication information.
400
Bad request.
401
Access denied.
401.1
Logon failed. The logon attempt is unsuccessful, probably because of a user name or password that is not valid.
401.2
Logon failed due to server configuration.
401.3
Unauthorized due to ACL on resource. This indicates a problem with NTFS permissions. This error may occur even if the permissions are correct for the file that you are trying to access. For example, you see this error if the IUSR account does not have access to the C:\Winnt\System32\Inetsrv directory.
401.4
Authorization failed by filter.
401.5
Authorization failed by ISAPI/CGI application.
401.7
Access denied by URL authorization policy on the Web server. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
403
Forbidden.
403.1
Execute access forbidden. The following are two common causes of this error message:
- You do not have enough Execute permissions. For example, you may receive this error message if you try to access an ASP page in a directory where permissions are set to None, or you try to execute a CGI script in a directory with Scripts Only permissions.
- The script mapping for the file type that you are trying to execute is not set up to recognize the verb that you are using (for example, GET or POST).
403.2
Read access forbidden. Verify that you have Read access to the directory. Also, if you are using a default document, verify that the document exists.
403.3
Write access forbidden. Verify that you have Write access to the directory
403.4
SSL required. Use HTTPS instead of HTTP to access the page.
403.5
SSL 128 required.
403.6
IP address rejected.
403.7
Client certificate required. You do not have a valid client certificate installed
403.8
Site access denied.
403.9
Too many users. The number of users who are connected to the server exceeds the connection limit.
403.10
Invalid configuration.
403.11
Password change.
403.12
Mapper denied access. The page that you want to access requires a client certificate, but the user ID that is mapped to your client certificate has been denied access to the file.
403.13
Client certificate revoked.
403.14
Directory listing denied.
403.15
Client Access Licenses exceeded.
403.16
Client certificate is untrusted or invalid.
403.17
Client certificate has expired or is not yet valid.
403.18
Cannot execute requested URL in the current application pool. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
403.19
Cannot execute CGIs for the client in this application pool. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
403.20
Passport logon failed. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
404
Not found. This error may occur if the file that you are trying to access has been moved or deleted.
404.0
File or directory not found.
404.1
Web site not accessible on the requested port.
404.2
Web service extension lockdown policy prevents this request.
404.3
MIME map policy prevents this request.
405
HTTP verb used to access this page is not allowed (method not allowed).
406
Client browser does not accept the MIME type of the requested page.
407
Proxy authentication required.
412
Precondition failed.
413
Request entity too large.
414
Request-URL too long.
415
Unsupported media type.
416
Requested range not satisfiable.
417
Execution failed.
423
Locked error.
500 Series
Server Error - The server cannot complete the request because it encounters an error.
500
Internal server error. You see this error message for a wide variety of server-side errors.
500.12
Application is busy restarting on the Web server. Indicates that you tried to load an ASP page while IIS was in the process of restarting the application. This message should disappear when you refresh the page. If you refresh the page and the message appears again, it may be caused by antivirus software that is scanning your Global.asa file.
500.13
Web server is too busy.
500.15
Direct requests for Global.asa are not allowed.
500.16
UNC authorization credentials incorrect. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
500.18
URL authorization store cannot be opened. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
500.100
Internal ASP error. You receive this error message when you try to load an ASP page that has errors in the code.
501
Header values specify a configuration that is not implemented.
502
Bad Gateway. Web server received an invalid response while acting as a gateway or proxy. You receive this error message when you try to run a CGI script that does not return a valid set of HTTP headers.
502.1
CGI application timeout.
502.2
Error in CGI application.
503
Service unavailable. This error code is specific to IIS 6.0.
504
Gateway timeout.
505
HTTP version not supported.
-
 R rick moved this topic from File assistance | Discussion on
R rick moved this topic from File assistance | Discussion on