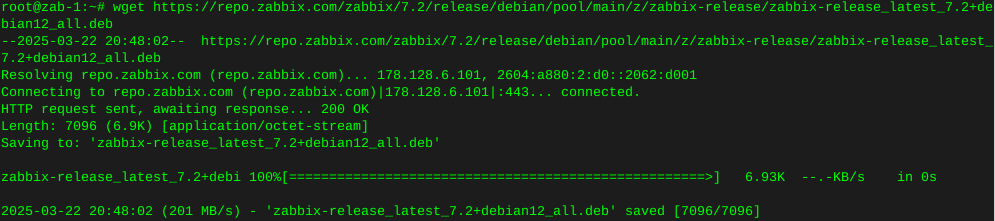
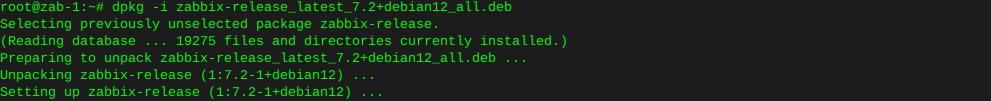
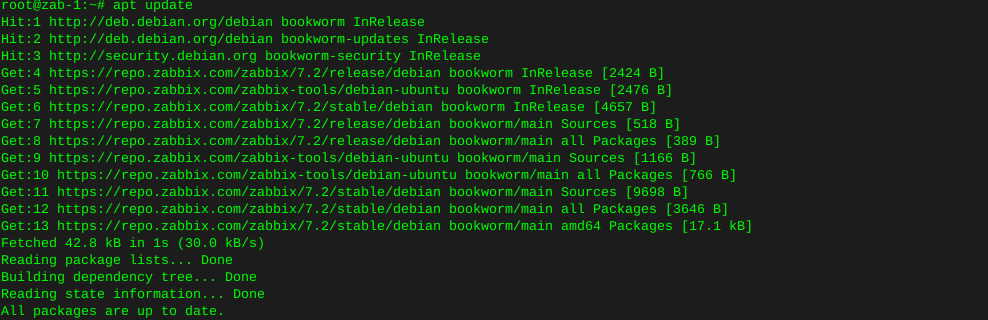
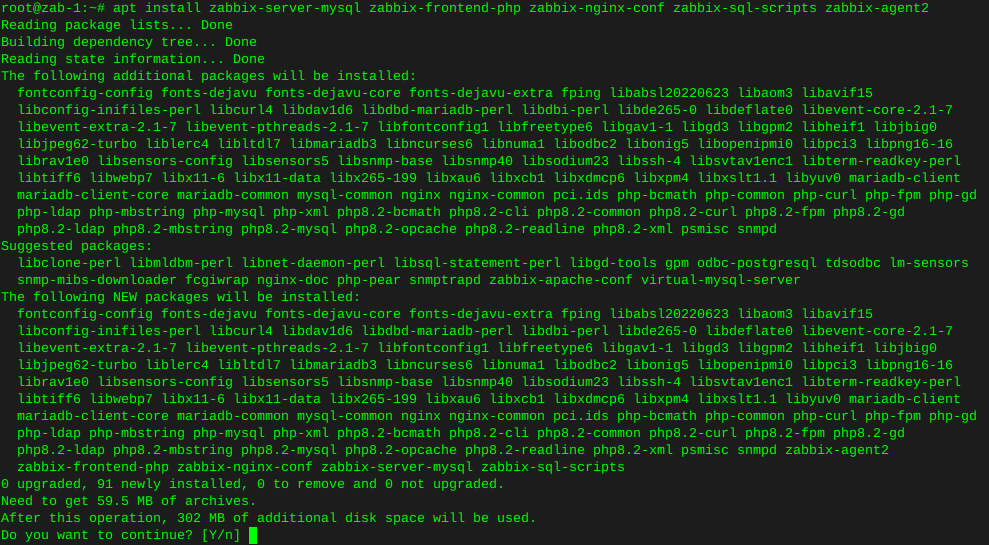
iperf test
-
iPerf3 from iPerf.fr:
-
iPerf3 is a tool for active measurements of the maximum achievable bandwidth on IP networks. It supports tuning of various parameters related to timing, buffers and protocols (TCP, UDP, SCTP with IPv4 and IPv6).
-
For each test it reports the bandwidth, loss, and other parameters. This is a new implementation that shares no code with the original iPerf and also is not backwards compatible.
-
iPerf was orginally developed by NLANR/DAST. iPerf3 is principally developed by ESnet / Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. It is released under a three-clause BSD license.
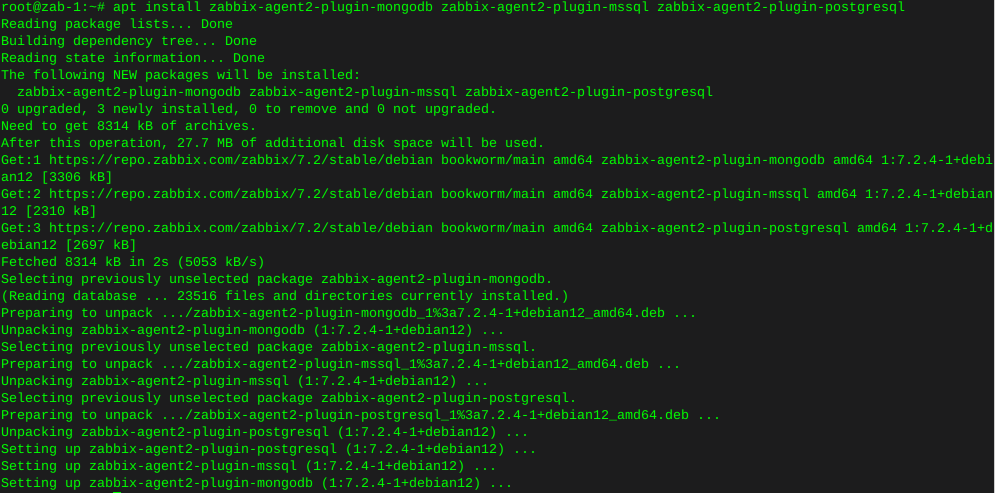
Install iperf Debian
apt-get install iperf3Starting a local server is not necessary if testing to a remote server.Example test server:
iperf -c ping.online.net -i 2 -t 20 -r
Start iperf server
To start Iperf in server mode, use the below command.
iperf -s
Start server in daemon mode
Running the server without daemon mode keeps the process running in the terminal. Use the -D switch to run it as a daemon in the background.
iperf -s -D
Connecting to server from client
Iperf needs to run on the local host in client mode, as well as in server mode on the remote host. To connect to the remote host, add it’s IP address after the -c switch.
iperf -c <ip or host/domain name>Bi-directional simultaneous (test the speed both ways at the same time)
Use the -d switch to test in the network bandwidth in both directions. This will perform two tests; one from local host to remote host, and another from the remote host to the local host.
iperf -c <ip or host/domain name> -d
Bi-directional testing (test the speed both one after another)
Use the -r switch to test in the network bandwidth in both directions. This is similar to -d except the tests will be performed in sequence; first from local host to remote host, and another from the remote host to the local host.
iperf -c <ip or host/domain name> -rChange the window size
The TCP window size can be changed using the -w switch followed by the number of bytes to use. the below example shows a window size of 2KB. This can be used on either the server or the client.
iperf -c <ip or host/domain name> -w 2048 iperf -s -w 2048
Change the port
You must use the same port on both the client and the server for the two processes to communicate with each other. Use the -p switch followed by the port number to use on both the local and remote host.
iperf -c <ip or host/domain name> -p 9000 iperf -s -p 9000
Change the test duration
The default test duration of Iperf is 10 seconds. You can override the default with the -t switch followed by the time in seconds the test should last.
iperf -s -t 60
UDP instead of TCP
The default protocol for Iperf to use is TCP. You can change this to UDP with the -u switch. You will need to run both the client and server in UDP mode to perform the tests.
iperf -s -u iperf -c -uThe result will have an extra metric for the packet loss which should be as low as possible, otherwise the packets will have to be re-transmitted using more bandwidth.
Run multiple threads
Iperf can spawn multiple threads to simultaneously send and receive data. Use the -P switch followed by the number of threads to use.
iperf -c -P 4
Check the version of Iperf
Use the -v switch to see the version of Iperf you have installed.
iperf -v
See the full list of arguments
Use the -h switch to see the full list of arguments supported by Iperf.
iperf -hA nice list of iPerf servers can be found at iPerf.fr
-